Arrange Your Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige
Chemical Composition
Botox, a popular aesthetic treatment, differs significantly from dermal fillers in terms of its **chemical composition** and mechanism of action.
Dermal fillers are made up of various materials such as **hyaluronic acid**, calcium hydroxylapatite, and poly-L-lactic acid, which are designed to restore lost volume, smooth out wrinkles, and enhance facial features. On the other hand, Botox is a neurotoxin derived from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum, responsible for causing botulism.
The active ingredient in Botox is a **protein called botulinum toxin type A**, which is produced through a process of fermentation and purification. This toxin works by temporarily paralyzing muscles, thereby reducing muscle activity and resulting in a smooth appearance.
In contrast, dermal fillers work by providing an immediate volume replacement, stimulating collagen production, and improving skin elasticity. The choice between Botox and dermal fillers depends on the individual’s concerns, skin type, and desired outcome.
One of the key differences between Botox and dermal fillers is their duration of action. Dermal fillers can last from a few months to several years, depending on the material used and individual factors. Botox, on the other hand, typically requires repeated injections every 3-4 months to maintain its effects.
Another significant difference lies in the injection technique. Dermal fillers are injected into the dermis, the layer of skin just beneath the epidermis, using a **quadrant injection technique** or a fanning motion. Botox, however, is administered via a fine needle, injecting the toxin into the **muscle fascia**, causing it to relax and resulting in a smooth appearance.
The choice between Botox and dermal fillers also depends on the specific concerns being addressed. For example, dermal fillers are often used for volume loss, lip augmentation, and facial rejuvenation, while Botox is commonly used for **axillary hyperhidrosis**, **blepharospasm**, and _facial wrinkles_.
In addition to these differences, Botox carries a higher risk of complications compared to dermal fillers. These risks include eyelid drooping (_ptosis_), facial asymmetry, and _mask-like facial expressions_. Dermal fillers also carry risks, but they are generally considered safer than Botox.
Despite these differences, both Botox and dermal fillers have revolutionized the field of aesthetic medicine, offering effective solutions for a range of cosmetic concerns. When choosing between these two treatments, it is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist to determine the best course of action for individual needs.
Botox, a popular aesthetic treatment, is derived from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum, which produces a neurotoxic protein complex that temporarily relaxes facial muscles.
This complex, composed of 150 amino acid residues, is also known as botulinum toxin A (BTA). The protein’s molecular structure is made up of three main components: the light chain, the heavy chain, and the accessory chain.
The light chain is responsible for the neurotoxic activity of Botox, while the heavy chain provides stability to the molecule. The accessory chain, also known as the C-terminal fragment, plays a role in the protein’s interaction with cells.
The chemical composition of Botox is characterized by its high molecular weight (approximately 150 kDa) and its acidic pH range (around 5-6). This unique combination allows it to effectively penetrate the skin and target specific nerve endings responsible for muscle movement.
From a biochemical perspective, Botox works by inhibiting the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that stimulates muscle contractions. By blocking this neurotransmitter, Botox causes muscles to relax, resulting in temporary paralysis or reduced muscle activity.
The mechanism of action is complex and involves multiple cellular pathways. Once injected into a targeted muscle, Botox binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), preventing the normal release of acetylcholine. This leads to a decrease in muscle contraction, resulting in a smooth, relaxed appearance.
Compared to dermal fillers, such as hyaluronic acid or calcium hydroxylapatite, Botox is a unique treatment that targets underlying muscle activity rather than filling in surface wrinkles and fine lines. This makes it an effective option for addressing dynamic facial expressions and muscle movements that contribute to aging.
Furthermore, the chemical composition of Botox allows it to be administered via a minimally invasive technique called a “botulinum toxin injection.” This involves inserting a small needle into the skin at specific locations to deliver the treatment directly to targeted nerve endings.
The long-term effects of Botox are due to its gradual breakdown and elimination by the body. While repeated injections are often necessary to maintain desired results, the temporary nature of this treatment makes it an attractive option for patients seeking a minimally invasive solution for aesthetic concerns.
Botox is a popular aesthetic treatment used to temporarily relax facial muscles and reduce the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
The active ingredient in Botox, botulinum toxin, works by inhibiting nerve signals to the muscles, thereby relaxing them and reducing muscle activity.
This process occurs when the toxin binds to the nerve terminals at the neuromuscular junction, blocking the release of a chemical messenger called acetylcholine.
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that signals the muscle to contract; without it, the muscle remains relaxed and cannot contract.
When Botox is injected into a muscle, it blocks nerve impulses from traveling to that muscle, resulting in reduced muscle tone and activity.
This reduction in muscle activity can lead to a decrease in wrinkle depth and a smoother appearance of the skin.
The effects of Botox are temporary, lasting anywhere from 3-6 months, after which the muscles return to their normal state and the wrinkles reappear.
The duration of action can vary depending on the individual, the location of the injection, and the dose used.
In comparison to dermal fillers, Botox is a dynamic treatment that addresses the movement and relaxation of facial muscles, whereas dermal fillers focus on restoring lost volume with materials such as hyaluronic acid or collagen.
Dermal fillers can provide immediate results, but their effects are also temporary and may require repeated injections to maintain the desired appearance.
Botox is often used in conjunction with dermal fillers, however, as it can be used to enhance the results of filler treatments by relaxing surrounding muscles that could cause the treated area to wrinkle or crease.
For example, Botox can be used to relax the forehead muscles while filling in fine lines and wrinkles between the eyebrows with dermal fillers like Juvederm or Restylane.
This combination of treatments provides a more comprehensive approach to achieving smooth, youthful-looking skin.
In contrast to dermal fillers, Botox does not add volume; instead, it modifies the appearance of existing wrinkles and fine lines by relaxing the muscles that cause them.
The unique mechanism of action of botulinum toxin makes Botox a versatile treatment option for a range of aesthetic concerns, from forehead wrinkles to crow’s feet and lip lines.
Mechanism of Action
Dermal fillers, specifically those composed of _Hyaluronic Acid_, are a type of aesthetic treatment used to restore lost volume and smooth out wrinkles and fine lines on the face. Unlike Botox injections, which temporarily paralyze muscle activity to prevent wrinkles from forming, dermal fillers work by replenishing lost collagen and elastin in the skin.
The mechanism of action of _Hyaluronic Acid_ fillers is based on its ability to retain water molecules, which allows it to expand and fill in hollows and defects in the skin. When injected into a targeted area, the acid-based filler particles are rapidly absorbed by the body’s immune system, where they are broken down and eliminated.
However, before reaching the bloodstream, the _Hyaluronic Acid_ filler particles stimulate the body to produce new collagen and elastin fibers, a process called neo-synthesis. This leads to an increase in skin elasticity and firmness, resulting in a more youthful appearance.
The effectiveness of dermal fillers is largely dependent on their ability to promote collagen production and maintain moisture levels within the skin. This makes them particularly effective for treating nasolabial folds, marionette lines, and other facial wrinkles caused by volume loss.
To achieve optimal results, dermal fillers are administered using a range of techniques, including nanofillers-injected using tiny needles or cannulas, and microneedling combined with filler injection. The choice of technique depends on the specific application and individual patient needs.
A key advantage of dermal fillers is their reversibility. If a filler is injected inappropriately or in an area where it’s not needed, it can be easily dissolved by an enzyme called hyaluronidase, which breaks down the _Hyaluronic Acid_ molecules without causing significant harm.
However, like any cosmetic treatment, dermal fillers carry potential side effects and complications, such as symptomatic facial edema, skin reactions at the injection site, or rare cases of allergic reactions. Therefore, it’s essential for patients to choose a reputable provider who follows established safety guidelines.
In conclusion, while Botox and dermal fillers differ in their mechanisms of action, both treatments play distinct roles in the aesthetic industry. Dermal fillers provide an attractive solution for restoring lost volume and rejuvenating facial appearance through the use of Hyaluronic Acid-based fillers.
By understanding the unique benefits and potential risks associated with dermal fillers, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment options and achieve optimal results in maintaining a youthful and radiant appearance.
Hyaluronic acid and calcium hydroxylapatite are two popular components used in dermal fillers, which are substances injected into the skin to restore lost volume, smooth out wrinkles, and enhance facial appearance.
**Hyaluronic Acid** is a naturally occurring substance found in the body, particularly in connective tissue. It’s a glycosaminoglycan (GAG) that plays a crucial role in maintaining skin hydration and elasticity. Derivatives of hyaluronic acid, such as **HA fillers**, are widely used to add volume to the face, smooth out wrinkles, and improve facial contours.
The mechanism of action of HA fillers involves the injection of the substance into the dermal tissue, where it’s metabolized by enzymes. As the hyaluronic acid is broken down, water is retained in the surrounding tissues, resulting in a temporary increase in skin hydration and volume. This effect can last for several months, depending on the individual’s skin type, facial anatomy, and the specific product used.
**Calcium Hydroxylapatite**, on the other hand, is a mineral component that makes up a significant portion of bone tissue. **CaHA fillers**, derived from this mineral, are known for their durability and long-lasting effects. When injected into the skin, calcium hydroxylapatite particles stimulate collagen production, which helps to improve facial structure and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
The mechanism of action of CaHA fillers involves the formation of a calcium-phosphate complex with water molecules in the dermal tissue. This process, known as *calcification*, results in the gradual release of calcium ions, which stimulate collagen synthesis and improve skin texture and density.
Unlike **Botulinum Toxin**, another popular aesthetic treatment, HA and CaHA fillers work by stimulating the body’s natural processes to produce more collagen, rather than temporarily paralyzing facial muscles. This fundamental difference in mechanism of action is a key distinction between Botox and dermal fillers.
When choosing between Botox and HA or CaHA fillers, patients should consider their individual needs and goals. Botox is ideal for treating dynamic wrinkles, such as those caused by facial expressions, whereas HA and CaHA fillers are better suited for adding volume to the face, smoothing out wrinkles, and enhancing facial contours.
In terms of duration of effect, HA fillers typically last between 6-12 months, depending on the individual’s skin type and facial anatomy. CaHA fillers can last up to two years or more, making them a popular choice for patients seeking longer-lasting results.
Overall, while both Botox and dermal fillers are effective aesthetic treatments, their mechanisms of action, benefits, and duration of effect differ significantly. Patients should consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment for their individual needs and goals.
The mechanism of action for dermal fillers, including those used to treat facial wrinkles and folds, involves a process by which these substances interact with the skin to provide volume and moisture.
When injected into the skin, dermal fillers such as hyaluronic acid, calcium hydroxylapatite, and poly-L-lactic acid come into contact with the collagen and elastin fibers that give structure to the skin.
These substances then bind to these fibers, causing them to swell and fill in the wrinkles and folds that they touch.
This swelling of the collagen and elastin fibers serves to restore lost volume and texture to the skin, resulting in a more youthful appearance.
In contrast to Botox, which works by temporarily relaxing muscles to reduce facial expressions that cause wrinkles and fine lines, dermal fillers work by actively adding volume and moisture to the skin.
This difference in mechanism of action is one reason why dermal fillers can be used to treat a wider range of concerns than Botox, including wrinkles, folds, and dryness.
Dermal fillers can also be used to enhance lip shape and size, augment cheekbones, and even restore lost fat volume in the face.
However, it’s worth noting that dermal fillers are not as long-lasting as Botox, which is typically effective for 3-4 months before needing to be repeated.
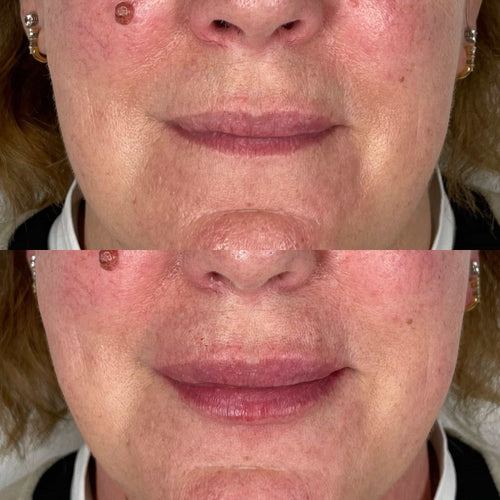
Dermal fillers, on the other hand, can last anywhere from a few months to several years depending on the type of filler used and individual factors such as skin texture and lifestyle.
The choice between Botox and dermal fillers ultimately depends on the specific concerns being treated and the desired outcome.
In some cases, a combination of both treatments may be necessary to achieve the best results.
It’s also worth noting that there are many different types of dermal fillers available, each with its own unique characteristics and potential benefits.
Hyaluronic acid fillers, for example, are popular for their ability to hold large amounts of water, making them particularly well-suited for treating dry or dehydrated skin.
Calcium hydroxylapatite fillers, on the other hand, are often used for more structural concerns, such as hollow cheeks or sagging eyelids.
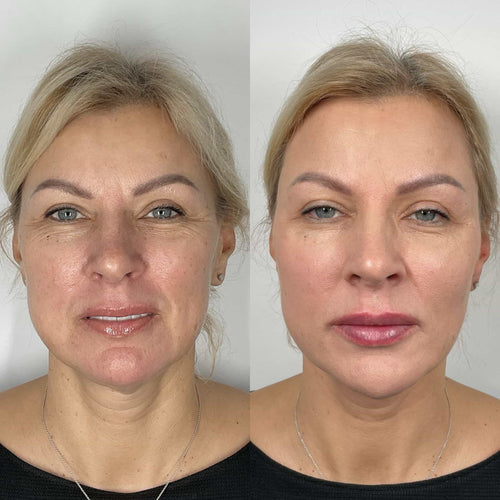
Poly-L-lactic acid fillers, meanwhile, have been shown to stimulate collagen production over time, making them a popular choice for patients looking to address signs of aging from multiple angles.
Effects and Duration
Botox, a popular cosmetic treatment, works by injecting tiny amounts of _Botulinum Toxin_ (Botox) into specific areas of the face or body to temporarily relax facial muscles and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
The localized anesthetic effect of Botox is primarily due to its ability to bind to and block the release of *_Acetylcholine_* (a neurotransmitter), thereby inhibiting muscle contractions. This results in a reduced level of muscle activity, which can help to smooth out facial expressions and reduce the appearance of dynamic wrinkles.
The duration of Botox’s effects can vary depending on several factors, including the dosage used, the individual’s metabolism, and the specific treatment area. On average, the effects of Botox can last anywhere from 3 to 6 months, with some cases lasting longer or shorter.
During this time, the treated muscles remain relaxed, reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles caused by repetitive muscle contractions. In contrast, dermal fillers work by _hyaluronic acid_ injections to provide temporary volume augmentation, but they do not have a localized anesthetic effect on facial muscles.
Botox’s duration of action is typically divided into three phases:
Phase 1: The initial effects of Botox can be seen within 3-7 days after treatment, with the peak effect occurring around 2-4 weeks post-injection. During this phase, the muscles are relaxed, and fine lines and wrinkles begin to appear smoother.
Phase 2: After 6-12 months, the effects of Botox start to wear off gradually, with some residual paralysis remaining in the treated muscles. This is due to the gradual degradation of _Botulinum Toxin_ over time.
Phase 3: After 1-2 years, the residual paralysis from Phase 2 starts to resolve, and muscle function returns to normal. However, this does not necessarily mean that the effects of Botox are completely gone; some studies suggest that the benefits of Botox can persist even after several years.
It’s worth noting that repeated injections of Botox can lead to a gradual decrease in its effectiveness over time. This is due to the development of _antibodies_ by the body against the _Botulinum Toxin_, which can neutralize its effects and reduce its ability to relax facial muscles.
Despite this, Botox remains one of the most popular cosmetic treatments for reducing fine lines and wrinkles, with millions of injections performed worldwide each year. Its localized anesthetic effect and relatively short duration of action make it a convenient option for patients seeking non-invasive, long-term results.
Botox effects are typically short-lived, with most people noticing a decline in its efficacy between three to six months after treatment.
Book a Dermal Filler Session with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
However, some studies have suggested that Botox can remain effective for up to nine months, although this is not universally accepted and may vary depending on individual factors.
The duration of Botox effects can be influenced by several factors, including the size and location of the treated area, as well as the patient’s overall health and lifestyle.
For example, patients who smoke or have certain medical conditions may experience a shorter duration of efficacy from Botox injections.
Additionally, the type of muscle being targeted by Botox can also impact its longevity.
Muscles that are more prone to overactivity, such as those used for facial expressions like frowning or scowling, may require more frequent treatment with Botox to maintain desired effects.
On the other hand, muscles that are less active, such as those involved in eyebrow movements or eyelid lifting, may experience a longer duration of efficacy from Botox injections.
The effects of Botox can also be influenced by individual factors, such as age and genetics.
For example, younger patients may experience faster metabolism of Botox, which could lead to shorter durations of efficacy compared to older patients.
Furthermore, certain genetic conditions or diseases may affect the way Botox works in the body, leading to variations in its duration of effect.
As a result, it’s essential for patients to work closely with their healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan and timeline for achieving desired results with Botox injections.
In contrast to dermal fillers, which can provide longer-lasting effects that last anywhere from one to five years or more, Botox is a more temporary solution that requires periodic maintenance treatments.
This makes it an ideal choice for patients who are looking for a quick and non-invasive way to address specific facial concerns or wrinkles.
Dermal fillers, such as hyaluronic acid, calcium hydroxylapatite, and poly-L-lactic acid, are designed to restore lost facial volume, smooth out wrinkles, and enhance lip augmentation. While they can provide relatively long-lasting results, the effects of dermal fillers can vary in duration depending on the type of filler used and individual factors.
For hyaluronic acid fillers, such as Juvederm and Restylane, the effects typically last between 6 to 12 months, with some studies showing an average duration of around 9 months. However, this can vary depending on the specific product, the location treated, and individual factors such as skin type and lifestyle.
Calcium hydroxylapatite fillers, like Radiesse, tend to provide longer-lasting results, lasting up to 18 months or more in some cases. This is due to their unique composition, which allows them to integrate with the body’s own collagen production over time.
Poly-L-lactic acid fillers, such as Sculptra, offer a more permanent solution by stimulating collagen production, which can lead to sustained results lasting up to 2-3 years or even longer. However, this process requires multiple treatments and can be more time-consuming than traditional dermal fillers.
The duration of effects can also be influenced by various factors such as lifestyle choices, skin care habits, and environmental conditions. For example, individuals who smoke may experience faster degradation of hyaluronic acid fillers due to the harsh effects of cigarette smoke on collagen production and tissue health.
Additionally, repeated treatments may be necessary to maintain optimal results with dermal fillers, as the natural degradation of the filler material over time can lead to a gradual loss of volume or correction of wrinkles. This highlights the importance of regular maintenance sessions and open communication between patients and practitioners to ensure optimal outcomes and minimize downtime.
It is essential for individuals considering dermal fillers to have realistic expectations about their duration of effects, as well as any potential risks or side effects associated with repeated treatments. By understanding these factors, patients can make informed decisions about their aesthetic treatment plans and work closely with their practitioners to achieve the best possible results.
Get a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige at It’s Me and You Clinic
In contrast, Botox injections typically provide a more immediate and rapid onset of effects, often lasting between 3-6 months, although some studies have shown longer-lasting results. Botox works by temporarily paralyzing muscles responsible for wrinkles, providing a quick and effective solution for fine lines and frown lines.
The duration of effects with Botox can vary depending on factors such as muscle mass, skin type, and individual metabolism. In general, repeated Botox injections are necessary to maintain optimal results, but the process is relatively straightforward and can be incorporated into regular maintenance sessions for other aesthetic treatments.
Read more about The CBD Consultancy here. Read more about W1 Wellness here. Read more about Cleveland Relationship Therapy here. Read more about Clover Design Online here. Read more about Apples and Pears Co. here.
- Juvederm Volite Skin Booster Treatments Near Mitcham, Surrey - May 8, 2025
- Exosome Therapy For Skin Rejuvenation Near Caterham, Surrey - May 8, 2025
- How Satin Pajamas Double As Sexy Lingerie - May 7, 2025
